Private Cloud Deployment Guide
This guide walks you through deploying Cequence AI Gateway to your private cloud Kubernetes clusters. You'll learn how to create pools from the UI and deploy using the CLI.
Overview
The deployment process consists of four main steps:
- Create a Pool - Configure your Kubernetes cluster settings through the UI
- Install the CLI - Download and set up the AI Gateway CLI tool
- Verify Cluster Permissions - Check and configure required RBAC permissions
- Deploy to Cluster - Use the CLI to deploy AI Gateway to your private cloud cluster
Part 1: Creating a Pool from the UI
A pool represents a Kubernetes cluster where AI Gateway will be deployed. Pools define cluster-specific configurations like namespace, resource limits, ingress settings, and more.
Prerequisites
- Access to the Cequence AI Gateway UI with Tenant Admin or Tenant User role
- Basic understanding of Kubernetes concepts (namespaces, ingress, resources)
UI Overview: Private Cloud Page
The Private Cloud page is your central hub for managing pools. When you navigate to Private Cloud from the left sidebar, you'll see one of two states:
Empty State (No Pools Created Yet):
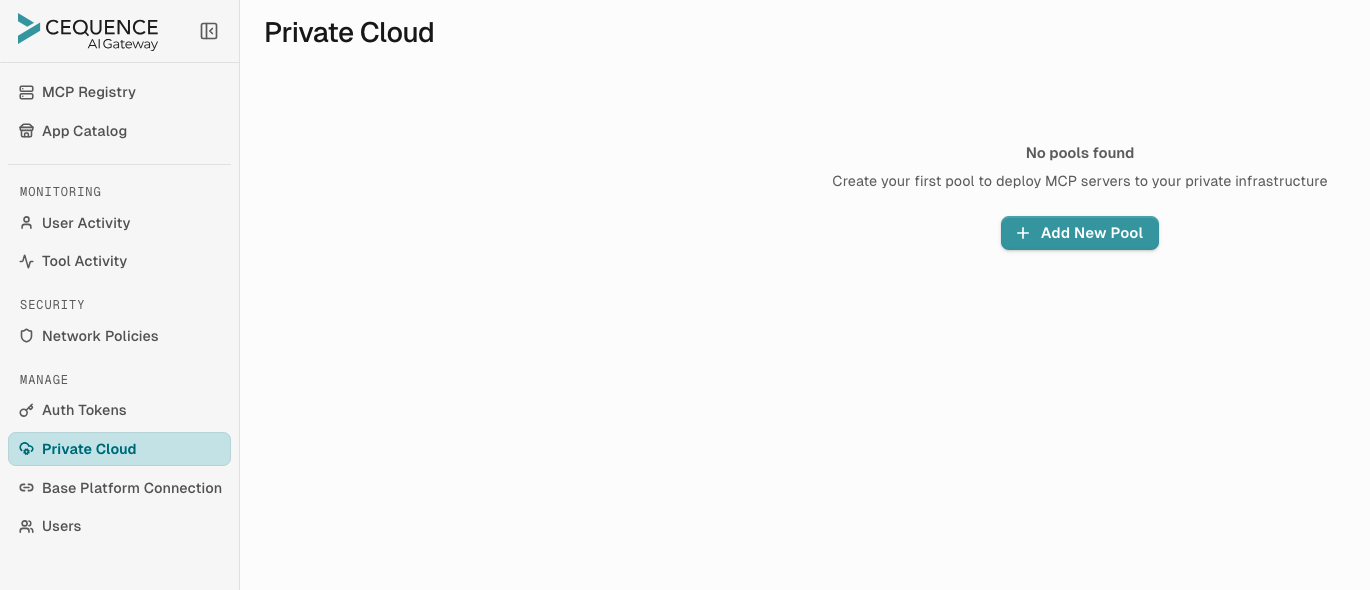
- Centered message: "No pools found"
- Instructional text: "Create your first pool to deploy MCP servers to your private infrastructure"
- Large "Add New Pool" button with a plus icon (+), prominently displayed in the center
Pools List View (After Creating Pools):
-
Header Section:
- Add New Pool button - Opens the pool creation dialog
- Status Filter dropdown - Filter pools by status (All, Active, Inactive)
-
Pools List/Table: Each pool entry displays:
- Pool Name & Version (e.g., "Production Cluster v1")
- Pool ID - Short unique identifier (e.g., "abc123xyz")
- Servers Count - Number of MCP servers deployed in this pool
- Status - Active (has running servers) or Inactive (no servers)
- Last Active - Timestamp of last activity (e.g., "2:30 PM (1h)", "Never")
Step-by-Step: Creating a Pool
-
Navigate to Private Cloud
- Log in to the Cequence AI Gateway UI
- Click on Private Cloud in the left navigation menu
UI Reference: The Private Cloud option appears in the left navigation sidebar. Clicking it will take you to the Private Cloud page.
-
Open Create Pool Dialog
- If you have no pools yet, you'll see an empty state with:
- Centered message: "No pools found"
- Instructional text: "Create your first pool to deploy MCP servers to your private infrastructure"
- Large "Add New Pool" button with a plus icon in the center
- If you already have pools, you'll see a list of pools with an Add New Pool button at the top
- Click the Add New Pool button
- The "Create New Pool" dialog will open with four configuration tabs at the top:
- Basic Information (selected by default)
- Resource Configuration
- Ingress Configuration
- Advanced
UI Reference: The Create New Pool dialog is a modal window with:
- Title: "Create New Pool" at the top
- Close button (X) in the top right corner
- Four tabs for different configuration sections
- Form fields in the currently selected tab
- Action buttons at the bottom: "Cancel" (outlined) and "Create Pool" (primary button)
- If you have no pools yet, you'll see an empty state with:
-
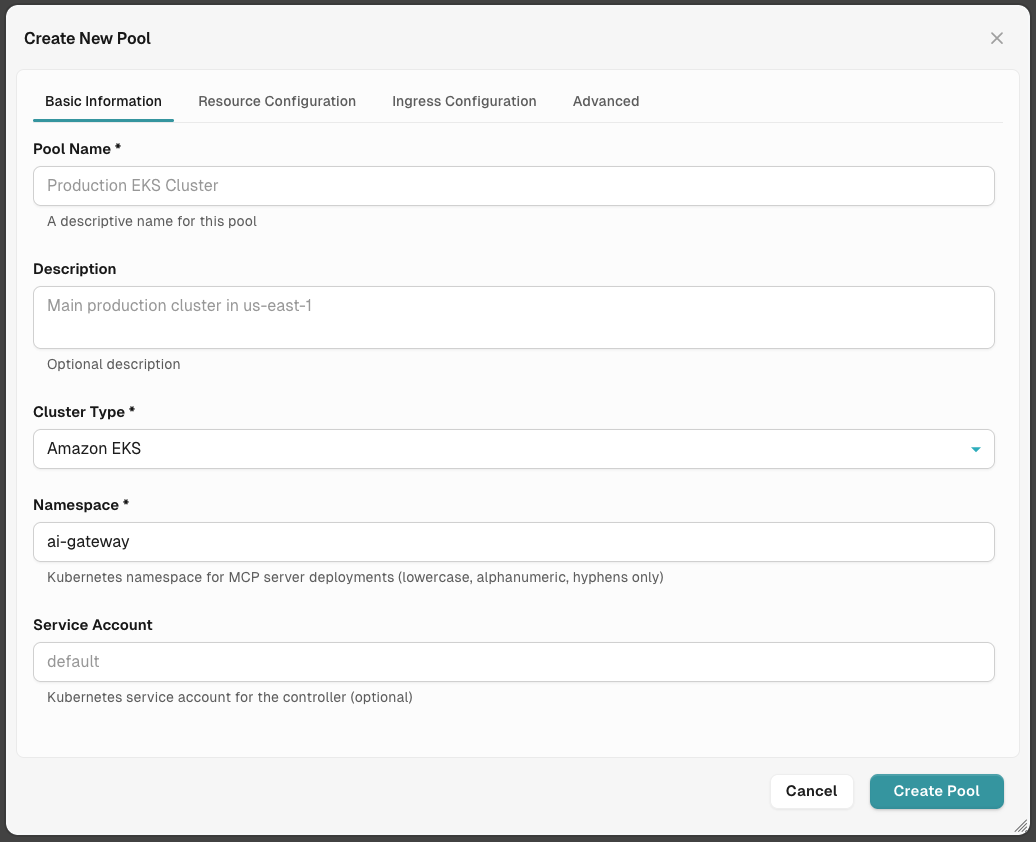
Configure Basic Information (Tab 1)
The "Basic Information" tab is selected by default when the dialog opens. Fill in the following fields:
UI Reference: The Basic Information tab shows:
- Pool Name field (required, marked with *) with helper text: "A descriptive name for this pool"
- Description multi-line text area (optional) with helper text: "Optional description"
- Cluster Type dropdown (required, marked with *) showing options: Amazon EKS, Azure AKS, Google GKE, Native Kubernetes
- Namespace field (required, marked with *) with helper text: "Kubernetes namespace for MCP server deployments (lowercase, alphanumeric, hyphens only)"
- Service Account field (optional) with helper text: "Kubernetes service account for the controller (optional)"
Fill in the following required fields:
-
Pool Name (Required)
- Enter a descriptive name (e.g., "Production EKS Cluster", "Dev GKE Cluster")
- Example:
production-eks-us-west-2
-
Description (Optional)
- Add a description for this pool
- Example:
Production cluster for US West region workloads
-
Cluster Type (Required)
- Select your Kubernetes cluster type from the dropdown:
- Amazon EKS - Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service
- Azure AKS - Azure Kubernetes Service
- Google GKE - Google Kubernetes Engine
- Native Kubernetes - Standard Kubernetes cluster
- Select your Kubernetes cluster type from the dropdown:
-
Namespace (Required)
- Enter the Kubernetes namespace where MCP servers will be deployed
- Default:
ai-gateway - Must be lowercase, alphanumeric, and hyphens only (max 63 characters)
- Example:
ai-gatewayormcp-servers
-
Service Account (Optional)
- Specify a Kubernetes service account for the controller
- Leave empty to use the default service account
- Example:
aigateway-controller-sa
-
Configure Resource Configuration (Tab 2)
Set default resource limits for MCP server deployments:
-
Resource Requests
- CPU Requests: Minimum CPU allocation (e.g.,
100m,0.5,1)- Format: Numbers with optional 'm' suffix (millicores)
- Example:
100m(0.1 CPU cores)
- Memory Requests: Minimum memory allocation (e.g.,
128Mi,256Mi,1Gi)- Format: Numbers with unit suffix (Mi, Gi, M, G, Ki, K)
- Example:
128Mi(128 mebibytes)
- CPU Requests: Minimum CPU allocation (e.g.,
-
Resource Limits
- CPU Limits: Maximum CPU allocation (e.g.,
500m,1,2)- Example:
500m(0.5 CPU cores)
- Example:
- Memory Limits: Maximum memory allocation (e.g.,
512Mi,1Gi,2Gi)- Example:
512Mi(512 mebibytes)
- Example:
- CPU Limits: Maximum CPU allocation (e.g.,
-
Scaling Configuration
- Max Replicas: Maximum number of replicas per MCP deployment
- Range: 1-50
- Default:
5 - Example:
10for high-availability deployments
- Max Replicas: Maximum number of replicas per MCP deployment
Note: These are default values applied to all MCP servers deployed in this pool. Individual MCP servers can override these settings from the Edit Pool dialog under the "Resource Configuration" tab, which shows per-MCP resource overrides.
-
Configure Ingress Configuration (Tab 3)
Configure how MCP servers are exposed. Choose between two ingress modes:
- Enable Ingress (Toggle)
- Enable or disable ingress for MCP servers
- Default: Enabled
If ingress is enabled, first select the Ingress Mode:
Kubernetes Ingress Mode (Default)
Uses standard Kubernetes Ingress resources for routing.
-
Basic Settings
- Host: Ingress hostname for MCP servers
- Example:
mcp.example.comor*.mcp.example.com
- Example:
- Ingress Class Name: Any ingress controller class (free text input)
- Common values:
nginx,traefik,haproxy,kong,contour,ambassador - Cloud-specific:
alb(AWS),gce(GCP),azure-application-gateway - Example:
nginx
- Common values:
- Host: Ingress hostname for MCP servers
-
TLS/SSL Configuration
- Enable TLS: Toggle TLS/SSL encryption
- Default: Enabled
- TLS Secret Name (Optional): Kubernetes secret name containing TLS certificates
- Leave empty to use default naming convention
- Example:
mcpname-tls
- Enable TLS: Toggle TLS/SSL encryption
-
Ingress Annotations (Optional)
- Add custom annotations for ingress resources
- Common annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-prodnginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/force-ssl-redirect: "true"
- Click Add to add each annotation key-value pair
Istio Gateway Mode
Uses Istio Gateway and VirtualService for routing. Select this mode if your cluster uses Istio service mesh.
- Istio Configuration
- Gateway Name: Name of the shared Istio Gateway
- Default:
mcp-gateway
- Default:
- Gateway Namespace (Optional): Namespace for the Gateway
- Leave empty to use the same namespace as deployments
- VirtualService Name: Name of the shared VirtualService
- Default:
mcp-routes
- Default:
- Gateway Selector: JSON object for pod selector
- Default:
{"istio": "ingressgateway"} - Example:
{"app": "istio-ingressgateway"}
- Default:
- TLS Credential Name (Optional): TLS secret name for Gateway HTTPS
- HTTP Port (Optional): Gateway port for HTTP traffic
- Default:
80(can use custom ports like15305)
- Default:
- HTTPS Port (Optional): Gateway port for HTTPS traffic
- Default:
443
- Default:
- Gateway Name: Name of the shared Istio Gateway
Example Ingress Configuration:
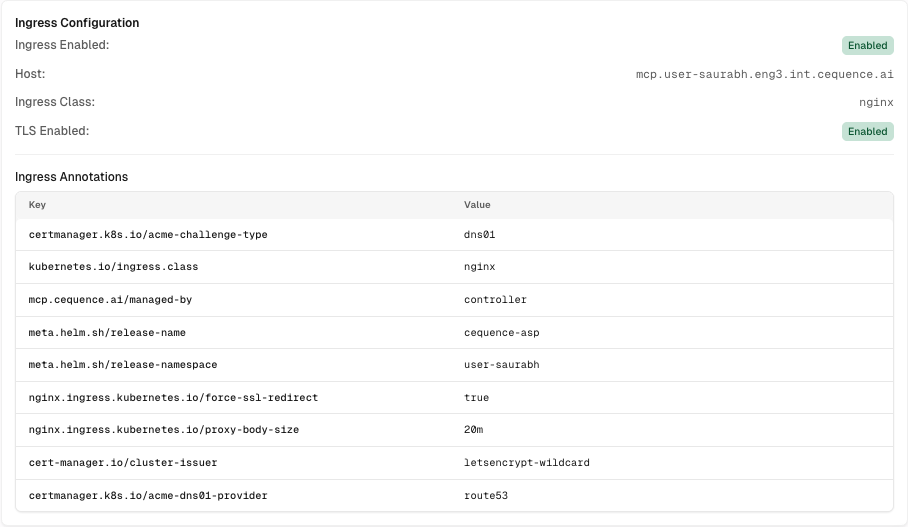
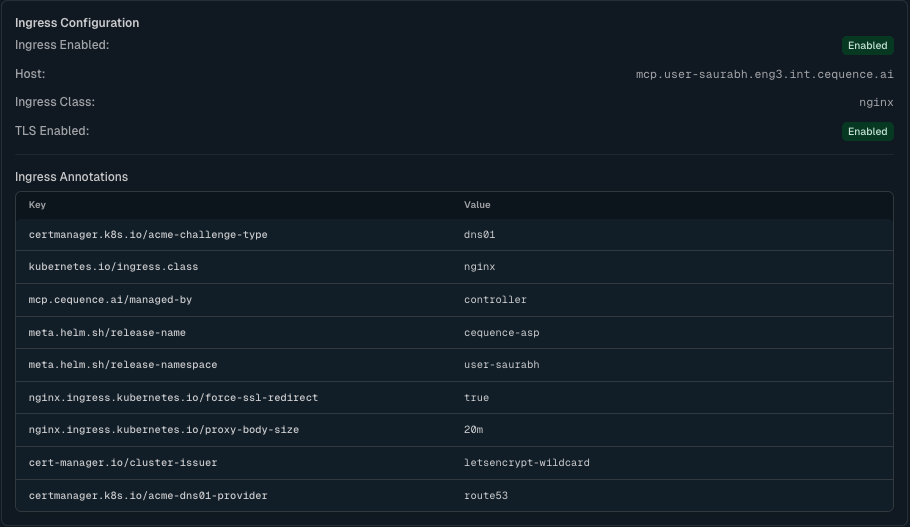
- Enable Ingress (Toggle)
-
Configure Advanced Settings (Tab 4)
-
Redis Configuration
Choose between two modes:
-
Auto-install (Recommended for new deployments)
- CLI will automatically install Redis in your cluster
- No additional configuration needed
-
Manual (For existing Redis deployments)
- Provide your own Redis connection details:
- Host: Redis server hostname or IP
- Example:
redisorredis.internal.company.com
- Example:
- Port: Redis server port
- Default:
6379
- Default:
- Username (Optional): Redis authentication username
- Password: Redis authentication password
- Database: Redis database number
- Default:
0
- Default:
- Enable TLS/SSL: Toggle TLS encryption for Redis connection
- Host: Redis server hostname or IP
- Provide your own Redis connection details:
-
-
Image Configuration (Pool-level settings)
Configure custom container images for this pool. Leave empty to use system defaults.
- MCP Server Image: Full Docker image path with tag
- Format:
registry/repository/image:tag - Example:
registry.gitlab.com/cequence/ai-gateway/releases/mcp-server:v110 - Example (custom registry):
123456789.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/ai-gateway/mcp-server:v110
- Format:
- Controller Image: Full Docker image path with tag
- Format:
registry/repository/image:tag - Example:
registry.gitlab.com/cequence/ai-gateway/releases/controller:v10
- Format:
Note: These settings are stored at the pool level. Each pool can have different image configurations. If left empty, the system defaults will be used (
mcp-server:v110andcontroller:v10). - MCP Server Image: Full Docker image path with tag
-
Pool Annotations (Optional)
Add custom Kubernetes annotations applied to all MCP deployments in this pool:
- Common annotations:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: ai-gateway-controllerenvironment: productionteam: platform
- Click Add to add each annotation key-value pair
- Common annotations:
-
-
Create the Pool
- Review all configurations across all tabs
- Click Create Pool button
- The pool will be created and appear in your Private Cloud pools list
UI Reference: After creating a pool, you'll be returned to the Private Cloud page where your new pool appears in the list. The pool entry shows:
- Pool name and version (e.g.,
your-pool-name v1) - Unique pool ID (short identifier like "abc123xyz")
- Number of servers deployed (initially 0)
- Status (Active/Inactive)
- Last active timestamp (shows "Never" for newly created pools)
You can filter pools by status using the Status dropdown at the top of the page.
Pool Configuration Summary
Here's a complete example configuration:
Basic Information:
- Name:
production-eks-us-west-2 - Description:
Production cluster for US West region workloads - Cluster Type:
Amazon EKS - Namespace:
ai-gateway - Service Account:
aigateway-controller-sa(optional)
Resource Configuration:
- CPU Requests:
100m - Memory Requests:
128Mi - CPU Limits:
500m - Memory Limits:
512Mi - Max Replicas:
5
Ingress Configuration:
- Enabled:
Yes - Mode:
Kubernetes Ingress(orIstio Gatewayfor service mesh) - Host:
mcp.example.com - Ingress Class:
nginx(any custom value supported) - TLS:
Enabled - TLS Secret:
mcp-tls-secret(optional)
Advanced Configuration:
- Redis Mode:
Auto-install - MCP Server Image:
registry.gitlab.com/cequence/ai-gateway/releases/mcp-server:v110(or leave empty for default) - Controller Image:
registry.gitlab.com/cequence/ai-gateway/releases/controller:v10(or leave empty for default)
Part 2: Installing the CLI
The AI Gateway CLI is a command-line tool for deploying and managing AI Gateway in private cloud clusters.
Official CLI Installation Page: https://cequence.gitlab.io/ai-gateway/cli/
Installation from GitLab Pages
The CLI can be installed directly from the official installation page:
Quick Install (Latest Stable Release):
curl -sSL https://cequence.gitlab.io/ai-gateway/cli/install.sh | sh
Install Latest Snapshot (Development Build):
curl -sSL https://cequence.gitlab.io/ai-gateway/cli/install.sh | sh -s -- snapshot
Install Specific Version:
curl -sSL https://cequence.gitlab.io/ai-gateway/cli/install.sh | sh -s -- v1.0.0
Installation Process
The installer will:
-
Detect your platform
- Automatically detects your OS (Linux, macOS, Windows) and architecture (x86_64, ARM64)
-
Download the appropriate binary
- Downloads the correct binary for your platform from GitLab Pages
- Supports Linux, macOS (Intel and Apple Silicon), and Windows
-
Install to system path
- Installs to
/usr/local/bin(or~/.local/binif no sudo access) - Makes the binary executable
- Installs to
-
Verify installation
- Runs
aigateway versionto confirm installation
- Runs
Manual Installation
If you prefer manual installation:
-
Download the binary from https://cequence.gitlab.io/ai-gateway/cli/
- Select your platform (Linux x86_64, Linux ARM64, macOS Intel, macOS Apple Silicon, Windows)
- Download the latest release or snapshot
-
Extract the archive
# Linux/macOS
tar -xzf aigateway_<version>_<OS>_<ARCH>.tar.gz
# Windows
unzip aigateway_<version>_Windows_<ARCH>.zip -
Move to PATH
# Linux/macOS
sudo mv aigateway /usr/local/bin/
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/aigateway
# Or without sudo
mkdir -p ~/.local/bin
mv aigateway ~/.local/bin/
export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH" -
Verify installation
aigateway version
Post-Installation Setup
After installation, initialize the CLI with your tenant and pool configuration.
Option 1: Copy Command from UI (Recommended)
If you have already created a pool in the UI, you can copy the complete initialization command directly from the pool detail page:
- Navigate to Private Cloud in the left sidebar
- Click on your pool to open the pool detail page
- Look for the "Pool Configuration Pending" banner at the top of the page
- Click the "Copy Command" button to copy the pre-filled command to your clipboard
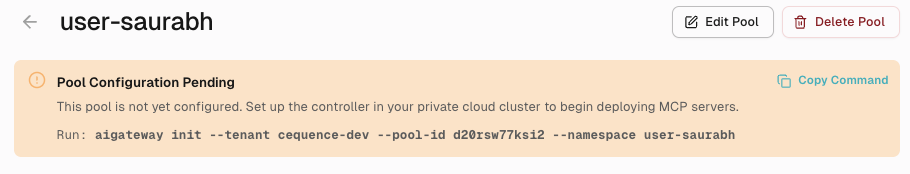
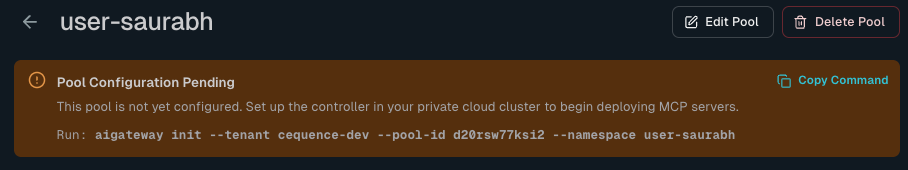
The copied command will include all required parameters:
aigateway init --tenant <your-tenant-id> --pool-id <your-pool-id> --namespace <your-namespace>
- Paste and run the command in your terminal
- Continue with authentication:
# Authenticate using OAuth device flow
aigateway login
# Verify configuration
aigateway config
Option 2: Manual Initialization
If you prefer to initialize manually or don't have a pool created yet:
# Initialize CLI with your tenant ID
aigateway init --tenant <your-tenant-id>
# Authenticate using OAuth device flow
aigateway login
# Verify configuration
aigateway config
Troubleshooting Installation
Issue: Binary not found after installation
- Check if the installation directory is in your PATH:
echo $PATH | grep -E "(/usr/local/bin|~/.local/bin)" - Add to PATH if needed:
# Add to ~/.bashrc, ~/.zshrc, or ~/.profile
export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"
Issue: Permission denied
- Make sure the binary is executable:
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/aigateway
Issue: Download fails
- Check network connectivity
- Verify GitLab Pages is accessible:
curl https://cequence.gitlab.io/ai-gateway/cli/ - Try installing from a different network or use a VPN
Part 3: Cluster Permissions
Before deploying AI Gateway, ensure you have the appropriate RBAC permissions in your Kubernetes cluster. This section covers the Deployer Permissions needed to run the aigateway CLI. The controller service account permissions are automatically created during deployment.
Required Permissions
The following resources and verbs are required in the target namespace:
Core Resources (Required)
| Resource | API Group | Verbs | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
deployments | apps | get, list, watch, create, update, patch, delete | Deploy controller and gateway components |
services | core | get, list, watch, create, update, patch, delete | Create service endpoints |
secrets | core | get, list, watch, create, update, patch, delete | Manage API credentials and registry secrets |
configmaps | core | get, list, watch, create, update, patch, delete | Store configuration data |
pods | core | get, list, watch | Monitor pod health and status |
events | core | get, list | View Kubernetes events for troubleshooting |
RBAC Resources (Required Unless Using Existing Service Account)
| Resource | API Group | Verbs | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
serviceaccounts | core | get, create, update, patch | Create controller service account |
roles | rbac.authorization.k8s.io | get, create, update, patch | Define controller permissions |
rolebindings | rbac.authorization.k8s.io | get, create, update, patch | Bind role to service account |
Note: If using an existing service account (configured in pool settings), only
getpermission is needed for these resources.
Optional Resources (Depending on Pool Configuration)
| Resource | API Group | Verbs | When Required |
|---|---|---|---|
statefulsets | apps | get, list, watch, create, update, patch, delete | If using StatefulSets for controller |
persistentvolumeclaims | core | get, create, update, patch | If using persistent storage or StatefulSets |
ingresses | networking.k8s.io | get, list, watch, create, update, patch, delete | If ingress is enabled in pool configuration |
horizontalpodautoscalers | autoscaling | get, list, watch, create, update, patch, delete | If autoscaling is configured |
Checking Permissions
Use the CLI to verify you have the required permissions:
# Check permissions for specific namespace
aigateway cluster permissions --namespace ai-gateway
# JSON output for automation
aigateway cluster permissions --namespace ai-gateway --json
Setting Up RBAC
If you lack sufficient permissions, generate and apply the required RBAC manifests:
Step 1: Generate Role
aigateway cluster permissions --generate-role --namespace ai-gateway > aigateway-deployer-role.yaml
Example generated Role:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: aigateway-deployer
namespace: ai-gateway
rules:
# Core Resources (Required)
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services", "secrets", "configmaps"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
# RBAC Resources (Required unless using existing service account)
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["serviceaccounts"]
verbs: ["get", "create", "update", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["roles", "rolebindings"]
verbs: ["get", "create", "update", "patch"]
# Optional Resources (include based on pool configuration)
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["statefulsets"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "create", "update", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["networking.k8s.io"]
resources: ["ingresses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
- apiGroups: ["autoscaling"]
resources: ["horizontalpodautoscalers"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
Step 2: Create RoleBinding
Bind the Role to your user or service account:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: aigateway-deployer-binding
namespace: ai-gateway
subjects:
- kind: User
name: your-username@company.com # Replace with your username
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: aigateway-deployer
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Step 3: Apply
kubectl apply -f aigateway-deployer-role.yaml
kubectl apply -f aigateway-deployer-rolebinding.yaml
For CI/CD: Use a ServiceAccount instead of User in the RoleBinding:
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: aigateway-deployer
namespace: ai-gateway
Skipping Permission Checks
Use the --skip-permission-checks flag if permission validation fails but you know you have the necessary permissions:
aigateway deploy install --skip-permission-checks
Warning: Only use this if you've verified your permissions. Deployment will fail if you lack required permissions.
Troubleshooting
Common Issues:
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
namespace not found | Have admin create namespace: kubectl create namespace ai-gateway |
roles.rbac.authorization.k8s.io is forbidden | Use existing service account or ask admin to create RBAC resources |
storageclasses is forbidden | Use --skip-permission-checks flag |
| Permissions not working after applying Role | Verify RoleBinding references correct user/namespace, wait for RBAC cache update |
Part 4: Deploying to Private Cloud Cluster
Once you've created a pool, installed the CLI, and verified your cluster permissions, you can deploy AI Gateway to your Kubernetes cluster.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes cluster access configured (
kubectlworking) - Pool created in the UI (see Part 1)
- CLI installed and authenticated (see Part 2)
- Appropriate RBAC permissions in the cluster
Step-by-Step: Deployment
-
Verify Cluster Access
# Check kubectl is configured
kubectl cluster-info
# Verify you can access the cluster
kubectl get nodes -
Initialize CLI Configuration
# Set your tenant ID
aigateway init --tenant <your-tenant-id> --pool-id <pool-id>
# Authenticate
aigateway login -
Deploy AI Gateway
Basic Installation:
# Deploy to default namespace (from pool configuration)
aigateway deploy installInstallation with Options:
# Deploy and wait for readiness
aigateway deploy install --wait
# Dry run to see what would be deployed
aigateway deploy install --dry-run
# Show processed manifests
aigateway deploy install --dry-run --show-manifestsAdvanced Installation:
# Custom service type (ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer)
aigateway deploy install --service-type LoadBalancer
# Custom storage class
aigateway deploy install --storage-class fast-ssd
# Skip CRD installation (if already installed)
aigateway deploy install --skip-crdsSkip Permission Checks:
Use the
--skip-permission-checksflag if you encounter permission errors like the following:[INFO] Performing comprehensive pre-flight validation...
[INFO] Both StatefulSet and Deployment detected for controller - StatefulSet permissions optional (will fallback to Deployment if needed)
Error: failed to apply manifests: pre-flight validation failed: failed to check storage classes: storageclasses.storage.k8s.io is forbidden: User "user@example.com" cannot list resource "storageclasses" in API group "storage.k8s.io" at the cluster scope# Skip permission checks
aigateway deploy install --skip-permission-checks -
Monitor Deployment
# Check deployment status
aigateway status
# Watch status in real-time
aigateway status --watch
# Detailed status information
aigateway status --verbose
# View logs
aigateway logs
# Follow logs for specific pod
aigateway logs aigateway-controller-0 --follow
# View events
aigateway events
# Monitor with comprehensive dashboard
aigateway monitor -
Verify Deployment
# Check pods are running
kubectl get pods -n <namespace>
# Check services
kubectl get svc -n <namespace>
# Check ingress (if configured)
kubectl get ingress -n <namespace>
# View controller logs
kubectl logs -n <namespace> deployment/ai-gateway-private-cloud-controller -f
Deployment Configuration
The CLI automatically:
- Fetches pool configuration from the API based on your tenant
- Applies cluster-specific settings (auto-detects storage class, service type)
- Injects credentials (API authentication, registry credentials)
- Validates permissions before deployment
- Processes manifests with tenant-specific values
Common Deployment Scenarios
Scenario 1: Standard Production Deployment
# Initialize and authenticate
aigateway init --tenant <your-tenant-id> --pool-id <your-pool-id>
aigateway login
# Deploy
aigateway deploy install
Scenario 2: Custom Configuration
# Deploy with custom settings
aigateway deploy install \
--replicas 5 \
--service-type LoadBalancer \
--storage-class gp3 \
--wait
Upgrading an Existing Deployment
# Upgrade to latest version
aigateway deploy upgrade
# Upgrade with specific options
aigateway deploy upgrade --replicas 5 --wait
# Check what would be upgraded
aigateway deploy upgrade --dry-run
Uninstalling
# Remove AI Gateway from cluster
aigateway deploy uninstall
# Dry run to see what would be removed
aigateway deploy uninstall --dry-run
Warning: Uninstalling will delete all resources including persistent data!
Troubleshooting Deployment
Issue: Deployment fails
# Check deployment status
aigateway status --verbose
# View error logs
aigateway logs --errors --since 10m
# Check Kubernetes events
aigateway events --critical
# Generate troubleshooting report
aigateway deploy troubleshoot
Issue: Pods not starting
# Check pod status
kubectl get pods -n <namespace>
# Describe problematic pod
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n <namespace>
# View pod logs
kubectl logs <pod-name> -n <namespace>
# Check events
kubectl get events -n <namespace> --sort-by='.lastTimestamp'
Issue: Image pull errors
- Verify registry credentials secret exists:
kubectl get secret regcred -n <namespace> - Check registry credentials are correct
- Verify network access to container registry
Issue: Ingress not working
- Verify ingress controller is installed:
kubectl get ingressclass - Check ingress resource:
kubectl get ingress -n <namespace>
kubectl describe ingress <ingress-name> -n <namespace> - Verify DNS configuration points to ingress
Post-Deployment Verification
After successful deployment, verify:
-
All pods are running:
kubectl get pods -n <namespace>
# Should show: ai-gateway-controller, redis (if auto-install), etc. -
Services are created:
kubectl get svc -n <namespace> -
Controller is healthy:
aigateway status
# Should show all components as healthy -
Logs are clean:
aigateway logs --errors
# Should show no errors
Best Practices
Pool Configuration
- Use descriptive names for pools (include environment and region)
- Set appropriate resource limits based on expected workload
- Enable TLS for production deployments
- Use auto-install Redis for simplicity, manual Redis for existing infrastructure
- Configure ingress annotations for production (cert-manager, SSL redirect, etc.)
CLI Usage
- Always use
--waitin production to ensure deployment completes - Use
--dry-runfirst to verify configuration - Monitor deployments with
aigateway status --watch - Keep CLI updated to latest version
- Use structured output (
--json) for automation
Security
- Store credentials securely (use Kubernetes secrets, not plain text)
- Use least-privilege RBAC (generate roles with
aigateway permissions --generate-role) - Enable TLS for all production deployments
- Regularly rotate API credentials and registry secrets
- Monitor access logs with
aigateway logs
Monitoring
- Set up alerts for unhealthy deployments
- Regular health checks with
aigateway status - Monitor logs for errors:
aigateway logs --errors - Track events for critical issues:
aigateway events --critical - Use
aigateway monitorfor comprehensive monitoring
Additional Resources
- CLI Documentation: See
cli/README.mdfor complete CLI reference - Pool Management: Edit pools from the UI after creation
- MCP Server Deployment: Once pool is configured, deploy MCP servers through the UI
- Troubleshooting: Use
aigateway deploy troubleshootfor detailed diagnostics
Summary
This guide covered:
- Creating pools from the UI with all configuration options
- Installing the CLI from GitLab Pages
- Verifying cluster permissions and setting up RBAC
- Deploying to clusters using the CLI
You should now be able to:
- Create and configure pools for your Kubernetes clusters
- Install and set up the AI Gateway CLI
- Check and configure required Kubernetes RBAC permissions
- Deploy AI Gateway to your private cloud clusters
- Monitor and troubleshoot deployments
For additional help, refer to the CLI help:
aigateway --help
aigateway deploy --help
aigateway status --help